
Recurring FedNow instant transactions
TodayPayments.com is the premier U.S. fintech platform offering seamless recurring payment automation over the FedNow® Service and RTP® Network.
Our solution empowers merchants of all sizes to streamline invoicing, automate real-time transactions, and gain treasury visibility with ISO 20022 smart messaging. We eliminate the delays, manual processes, and bank dependency—replacing them with certainty, scale, and 24/7 digital freedom.
Using Recurring FedNow® Instant and RTP® Payments with File Upload Automation
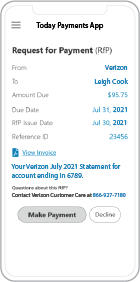
![]() Recurring payments are the backbone of
subscription services, B2B contracts, and client retainers. But
until recently, these payments were stuck in the slow lane—waiting
on ACH windows and banking delays. Now, U.S. merchants can take
control with real-time, recurring payment automation using
FedNow® and RTP® (Real-Time Payments).
Recurring payments are the backbone of
subscription services, B2B contracts, and client retainers. But
until recently, these payments were stuck in the slow lane—waiting
on ACH windows and banking delays. Now, U.S. merchants can take
control with real-time, recurring payment automation using
FedNow® and RTP® (Real-Time Payments).
With
TodayPayments.com, you can automate recurring invoicing, upload
FedNow® and RTP® payment files in batches, and ensure that clients,
vendors, and contractors receive funds instantly—with funding
certainty built in.
The future of invoicing is real-time, automated, and bank-agnostic. Whether you’re serving B2B clients, managing subscriptions, or collecting retainers, you can now send recurring FedNow® and RTP® payments using secure file uploads to any Credit Union or Financial Institution.
TodayPayments.com supports batch uploads of payment files in formats like .Excel, .XML, and .JSON, paired with ISO 20022-compliant Request for Payment (RfP) messages. Our software allows you to send one-time or recurring payments with precision and speed—no matter the institution or volume.
ISO 20022 Messaging and RfP Batch Uploads for All Credit Unions and Banks
You don’t need to wait on your bank to enable recurring payments. With TodayPayments.com, you can:
- Upload FedNow® and RTP® payment files to any bank or credit union.
- Use ISO 20022 RfP format to request payments or send payment data.
- Support B2B (Business-to-Business) and C2B (Consumer-to-Business) models.
- Enable recurring payment delivery via mobile links, text messages, or digital invoices.
- Guarantee funding certainty with real-time credit transfers and no reversals.
TodayPayments.com handles the heavy lifting so your accounting or treasury department can focus on automation, not complication.
Recurring Payment Automation with FedNow® and RTP® for U.S. Merchants
Whether you need weekly, monthly, or daily recurring payments, TodayPayments.com gives you enterprise-grade tools at small-business-friendly prices.
✔️ Features & Benefits for Merchants:
- 🔁 Recurring FedNow® & RTP® Payments — Easily automate repeat payments to clients, contractors, or service providers.
- 📂 Batch File Upload — Upload .Excel, .XML, or JSON files to initiate multiple real-time transactions in seconds.
- 🏦 Credit Union Compatibility — Works with all U.S. credit unions and financial institutions.
- 🧾 Digital Invoicing & RfP Messaging — Insert links or invoices directly into ISO 20022-compliant requests.
- 📲 Mobile, Text, and Email Delivery — Send RfPs to customers through any channel they prefer.
- 💵 Funding Certainty — Recipients receive funds instantly with no reversals.
- 🔄 Real-Time Treasury Reconciliation — Match payments to invoices automatically.
- 💼 Supports B2B and C2B Payments — Ideal for firms managing vendors, partners, or recurring service contracts.
For Recurring FedNow instant transactions, where payments occur repeatedly over a set period, both the payee (the entity receiving payment) and the payer (the entity making payment) need specific elements to ensure seamless processing. Here's how these elements might look for both parties:
Payee Side (Receiving Payment):
- Payment Request Identifier: A unique identifier assigned to each recurring payment request, allowing for tracking and management of individual transactions within the series of payments.
- Payment Amount: The fixed or variable amount to be received for each recurring transaction. This amount may remain constant for each payment or vary based on specific criteria.
- Payment Frequency: The interval at which payments are expected, such as daily, weekly, monthly, or custom intervals. This determines the schedule for recurring transactions.
- Payment Start Date: The date on which the recurring payments will commence. This ensures that payments begin at the designated time.
- Payment End Date (if applicable): The date on which the recurring payments will cease. This is optional and may be specified if there is a predetermined end to the payment schedule.
- Payment Instructions: Any specific instructions or details provided by the payee regarding the recurring payments, such as account information or payment terms.
Payer Side (Making Payment):
- Authorization: Confirmation from the payer indicating their consent to initiate the recurring payments as requested. This authorization may be provided upfront for the entire series of payments or may be required for each individual transaction, depending on the agreement between the payer and payee.
- Payment Frequency: The interval at which payments will be made, corresponding to the frequency specified by the payee. The payer ensures that payments are initiated according to the agreed-upon schedule.
- Payment Amount: The fixed or variable amount to be paid for each recurring transaction. The payer ensures that the correct amount is transferred for each payment.
- Payment Start Date: The date on which the recurring payments will commence, as specified by the payee. The payer initiates payments starting from this date.
- Payment End Date (if applicable): The date on which the recurring payments will cease, if specified by the payee. The payer ensures that payments are not initiated beyond this end date.
- Payment Execution: The actual transfer of funds from the payer's account to the payee's account for each recurring transaction. This may occur automatically according to the agreed-upon schedule.
By incorporating these elements into Recurring FedNow instant transactions, both the payee and the payer can effectively manage and process payments over time, ensuring accuracy, efficiency, and compliance with the agreed-upon payment terms.
Stop waiting on ACH. Stop chasing down clients.
And definitely stop relying on outdated banking systems.
With
TodayPayments.com, you can automate all your recurring FedNow® and
RTP® payments using smart file uploads and real-time reconciliation.
Whether you're processing one transaction or a thousand, your business
can run faster, smarter, and more profitably.
👉 Enroll now at TodayPayments.com and take your recurring invoicing into real-time—with certainty, speed, and 24/7 freedom.
Creation Recurring Request for Payment
We were years ahead of competitors recognizing the benefits of RequestForPayment.com. We are not a Bank. Our function as a role as an "Accounting System" in Open Banking with Real-TimePayments.com to work with Billers to create the Request for Payment to upload the Biller's Bank online platform. Today Payments' ISO 20022 Payment Initiation (PAIN .013) shows how to implement Create Real-Time Payments Request for Payment File up front delivering a message from the Creditor (Payee) to it's bank. Most banks (FIs) will deliver the message Import and Batch files for their company depositors for both FedNow and Real-Time Payments (RtP). Once uploaded correctly, the Creditor's (Payee's) bank continues through a "Payment Hub", either FedNow or RTP, will be the RtP Hub will be The Clearing House, with messaging to the Debtor's (Payer's) bank.
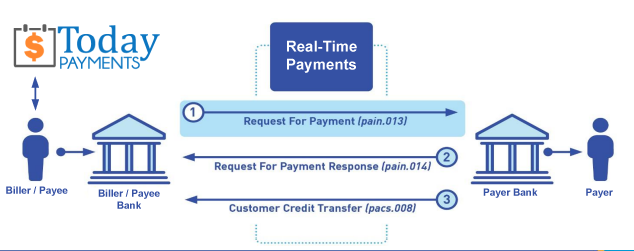
ACH and both Instant and Real-Time Payments Request for Payment
ISO 20022 XML Message Versions
The versions that
NACHA recommends for the Request for Payment message and the Response to the Request are pain.013 and pain.014
respectively. Version 5 for the RfP messages, which
The Clearing House Real-Time Payments system has implemented, may also be utilized as
there is no material difference in the schemas. Predictability, that the U.S. Federal Reserve, via the
FedNow ® Instant Payments, will also use Request for Payment. The ACH, RTP ® and FedNow ® versions are Credit Push Payments.
Payees ensure the finality of Instant Real-Time
Payments (IRTP) and FedNow using recurring Requests for
Payments (RfP), Payees can implement certain measures:
1.
Confirmation Mechanism:
Implement a confirmation mechanism to ensure that each
payment request is acknowledged and confirmed by the payer
before the payment is initiated. This can include requiring
the payer to provide explicit consent or authorization for
each recurring payment.
2.
Transaction Monitoring:
Continuously monitor the status of recurring payment
requests and transactions in real-time to detect any
anomalies or discrepancies. Promptly investigate and resolve
any issues that arise to ensure the integrity and finality
of payments.
3.
Authentication and
Authorization: Implement strong
authentication and authorization measures to verify the
identity of the payer and ensure that only authorized
payments are processed. This can include multi-factor
authentication, biometric verification, or secure
tokenization techniques.
4.
Payment Reconciliation:
Regularly reconcile payment transactions to ensure that all
authorized payments have been successfully processed and
finalized. This involves comparing transaction records with
payment requests to identify any discrepancies or
unauthorized transactions.
5.
Secure Communication Channels:
Utilize secure communication channels, such as encrypted
messaging protocols or secure APIs, to transmit payment
requests and transaction data between the payee and the
payer. This helps prevent unauthorized access or
interception of sensitive payment information.
6.
Compliance with Regulatory
Standards: Ensure compliance with
relevant regulatory standards and guidelines governing
instant payments and recurring payment transactions. This
includes adhering to data security requirements, fraud
prevention measures, and consumer protection regulations.
By implementing these measures, Payees can enhance
the finality and security of Instant Real-Time Payments
using recurring Requests for Payments, thereby minimizing
the risk of payment disputes, fraud, or unauthorized
transactions.
Each day, thousands of businesses around the country are turning their transactions into profit with real-time payment solutions like ours.

Contact Us for Request For Payment payment processing

